- |
- Inquiry List
- |
- Sign In or Sign Up
Carbide nozzle/cemented carbide nozzle/tungsten carbide nozzle
Tungsten carbide nozzle is made from hot pressing with straight bore and venture bore type. Due to its hardness, low density and excellent wear and anti-corrosion, Tungsten carbide nozzle has been widely used in sandblasting and shot peening equipment, offering a long life with optimum air and abrasive use.
About US:
With 20 years production experience,
1. We romise you the 100% raw material.
2. We quotation your order with 24 hours
3. We accept your order as per your requirements
Our guarantee:
1. 100% raw material.
2. Sintered in HIP Furnace
3. Size standard as per your requirements
4. Professional suggestion on products
5. Feedback within 24 hours
6. ISO9001: 2008 certificate.
7. Fully adopted in advance technology and equipment.
8. Professional manufacture for tungsten carbide items with 20 years experience.
9. Fully adopted in advance technology and equipment.
10. Quality Control System and strict inspection.
ALSO, we warmly welcome you and your drawing papers.
| Nozzle O.D.(mm) | 25.21 | 23.5 | 29.74 | 32.89 | 40.84 | Nozzle Recess diameter |
|
| Assemble Length(mm) |
34.8 | 19.05 | 20.62 | 26.97 | 26.97 | ||
| Type of Nozzle |
The series of diamond drill | Cone drill 5 5/8"-7 3/8" |
Cone drill 1/2"-8 1/" |
Cone drill 8 3/8"-13 3/4" |
Cone drill 14 3/4"-26" |
||
| Thread Type | Standard type | Standard type | Standard type | Stretch Type | |||
| SD-08 | S2-06 | S3-06 | S4-06 | S5-06 | 6.35 | ||
| SD-09 | S2-07 | S3-07 | S4-07 | S5-07 | 7.14 | ||
| SD-10 | S2-08 | S3-08 | S4-08 | S604-08 | S5-08 | 7.94 | |
| SD-11 | S2-09 | S3-09 | S4-09 | S604-09 | S5-09 | 8.73 | |
| S2-10 | S3-10 | S4-10 | S604-10 | 9.53 | |||
| SD-12 | S2-10A | S3-10A | S4-10A | S604-10A | S5-10A | 10.32 | |
| SD-13 | S2-11 | S3-11 | S4-11 | S604-11 | S5-11 | 11.11 | |
| SD-14 | S2-12 | S3-12 | S4-12 | S604-12 | S5-12 | 11.9 | |
| SD-15 | S2-13 | S3-13A | S4-13 | S604-13 | S5-13 | 12.7 | |
| SD-16 | S2-13A | S3-14 | S4-13A | S604-13A | S5-13A | 13.49 | |
| SD-17 | S2-14 | S3-15 | S4-14 | S604-14 | S5-14 | 14.29 | |
| SD-18 | S2-15 | S3-16 | S4-15 | S604-15 | S5-15 | 15.08 | |
| SD-19 | S2-16 | S3-17 | S4-16 | S604-16 | S5-16 | 15.88 | |
| SD-20 | S3-17A | S4-17 | S5-17 | 17 | |||
| SD-21 | S3-18 | S4-17A | S5-17A | 17.48 | |||
| SD-22 | S3-19 | S4-18 | S5-18 | 18.26 | |||
| S3-20 | S4-19 | S5-19 | 19.05 | ||||
| S3-20A | S4-20 | S5-20 | 19.84 | ||||
| S3-21 | S4-20A | S5-20A | 20.64 | ||||
| S3-22 | S4-21 | S5-21 | 21 | ||||
| S4-22 | S5-22 | 22.23 | |||||
| S4-23 | S5-23 | 23.02 | |||||
| S4-24 | S5-24 | 23.81 | |||||
For nozzles, tungsten Carbide nozzle is the most rugged and durable and provides the best value.
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a flow (especially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe via an orifice. For nozzles, tungsten Carbide nozzle is the most rugged and durable and provides the best value.
Tungsten carbide nozzle is made by the precision machining with the tungsten carbide materials (superhard alloy). The hardness reached over HRA90 degree while the anti-bending degree reached over 2300N/mm2. On machining tungsten carbide nozzle, we do the precision grinding and surface treatment to achieve Ra0.1 of the bore roughness and the Ra0.025 of the R place of both ends. There is a scientific curvature radius design in the both entrance. This design can ensure a smooth transit of the thread. Due to the overall materials processing, and no elevation in the bore, the phenomenon of easy-bending and plugging has been improved comparing with the ruby nozzle.
Tungsten carbide nozzle is made from hot pressing with straight bore and venturi bore type. Due to its hardness, low density and excellent wear and anti-corrosion, Tungsten carbide nozzle has been widely used in sandblasting and shot peening equipment, offering a long life with optimum air and abrasive use.
How to choose a tungsten carbide nozzle?
When choosing a tungsten carbide nozzle, consider the amount of available air in cfm, the capacity of the blast machine and the inside diameter of the piping, and the blast and air hoses. For optimal performance, these elements must be compatibly sized.
If too large a nozzle is used, low blast pressure and rapid wear on the blast hose will occur. If too small a nozzle is used, smooth media flow will be difficult to achieve.


1. What is MIM technology?
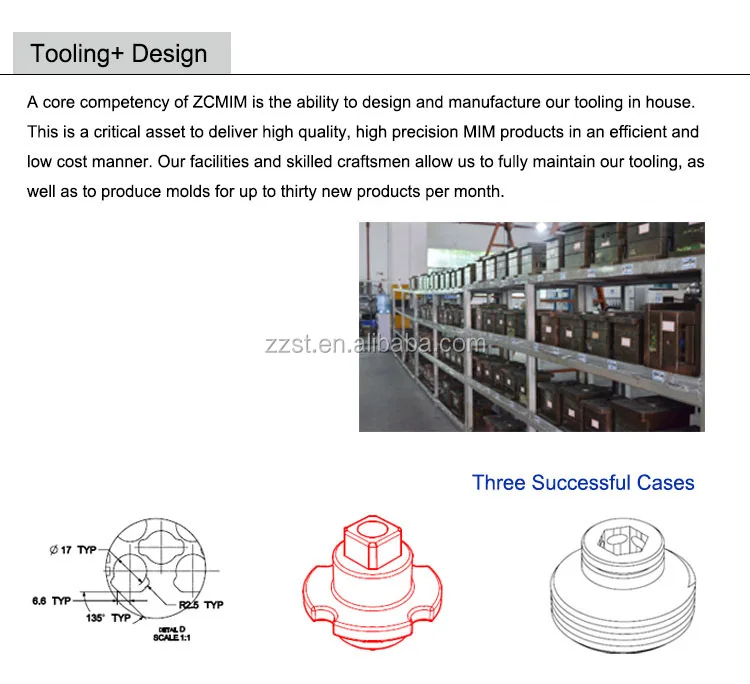
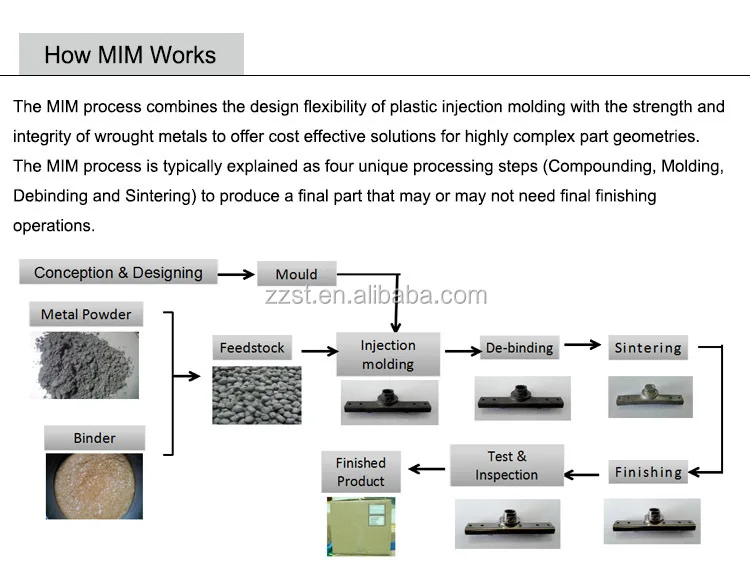
MIM (Metal Injection Molding) is a manufacturing technology that combines the shape making complexity of Plastic Injection Molding with the material flexibility of Powder Metallurgy.
2. Is the metal melted during the molding process?
No, only the binders are melted allowing the powders to flow like a plastic material. Upon cooling the binders solidify giving the part strength for handling. The part must be subsequently sintered to high density to achieve the required mechanical properties.
3. How does MIM differ from the Conventional PM process?
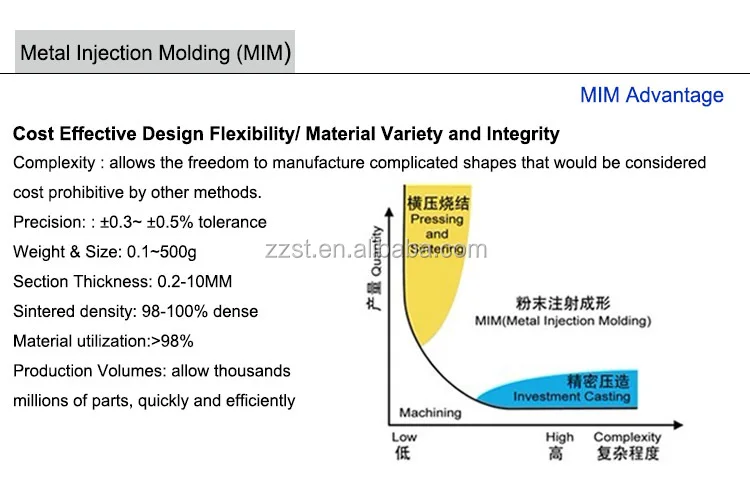
Conventional PM uses high, uniaxially applied pressure to coarse metal powders in a die set to produce moderately complex components. Typically, no further densification is gained during the sintering process. Densities achieved by this method are typically in the range of 80-90% of theoretical which limit the physical properties that can be achieved for the given alloy. MIM products are not limited in shape complexity due to the flexibility of the injection molding process. The fine metal powders used - combine with higher sintering temperatures to allow MIM to achieve near full density in the final article. This allows MIM products to have similar properties as wrought materials.
4. Does the part shrink during removal of binders?
No, the part will not change size in the debinding phase of the process. However, since sintering achieves near full density of the powders, the part will undergo a size change of up to 20%.
5. Why should I use MIM?
MIM excels in producing small, highly complex parts that are difficult or cost prohibitive to produce with conventional technologies such as machining or casting.